If you are an avid audiophile certainly you would have played with DAC. But do you know what is a DAC? how do DAC works? What are the processes happens inside it?
If you are curious to know then here is the complete guide on what is a DAC and its working.
Music is a form of art that's enjoyed by millions of people worldwide. There exists a vast array of audio equipment used to play music – from the smallest iPods to the largest stereo systems.
You might be an avid fan of good music, but have you ever wondered what processes occur inside a music player?
These days, music and other audio recordings are stored digitally as either MP3 or WAV files. But to listen for such music, it needs to be converted from digital format to analog signals – this conversion can only be handled by a Digital-to-Analog Converter.
What is a DAC?
DAC is an abbreviation for Digital to Analog Converter. You've probably heard the term "DAC" been thrown around when talking about audio electronics.
DAC definition:
A DAC simply refers to any system that receives digital signals and converts them into analog signals. Also denoted as D2A, Digital-to-Analog Converters usually handle an important role in transforming digital data into analog format.
DAC are wide-ranging and vary in quality, from the most sophisticated D2A systems to the most basic ones (such as those found in smartphones). Today, we have home theater DAC, headset DAC and even DAC speakers.
DACs are relatively advanced electronics whose purpose only became essential a few decades ago. Before the advent of DACs, music and other sounds were captured by a microphone and stored as analog signals.
People had to use gramophones to convert the analog data into sound using a needle that "sensed" the grooves.
These days, music files are stored in digital format – it's more convenient and takes up less space compared to analog storage techniques.
Digital signals are based on "zeros and ones" which is a unique language that computers and electronic devices comprehend.
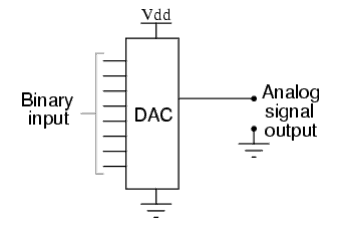
However, you'll need to convert this digital format into an analog signal whenever you want to listen to a digitally stored recording. Luckily, DAC chips are small and can be embedded into audio systems.
How does a DAC work?
A DAC operates using one simple principle: it converts digital pulses into analog signals using a series of integrated circuits.
Abstract numbers are transformed into a set of impulses and passed through a reconstruction filter that further processes those impulses using some unique interpolation techniques.
This process results in a smooth varying analog signal that is consequently converted into sound within the speaker element.
There are two categories of DACs:
- Internal DACs
- External (outboard) DACs
Internal Digital to Analog Converters perform the most basic function, but they're not too efficient when it comes to handling clocking errors.These often give rise to jittery sound.
Outboard DACs, on the other hand, are well equipped to handle and effectively eliminate clocking errors.
Digital bitstreams are reassembled into their analog equivalent more efficiently, helping to create a consistent sound that is jitter-free. Today, you can purchase a separate DAC card and incorporate it within your audiophile system.
Laptop and desktop computers utilize a unique outboard USB DAC whereas home stereo systems use a special home theatre DAC card.
However, you can also plug a USB DAC into your stereo system and it'll work just fine. You can also get a DAC for a headphone that improves the overall quality of your music when you're listening via headphones.
For your tablet or smartphone, you can buy an adaptor to support USB linking.
When buying an external DAC, it's important to consider your device. There's a plethora of DACs, some of which are designed for iPhone and Mac devices while others are meant for CD players, Android devices and PCs.
What does a DAC do?
Digital to Analog Converters are usually incorporated into audiophiles and stereo systems – although they're tiny circuits, they play a huge role in converting digital signals into analog formats.
These days, it's a common practice to store audio signals in digital formats. CDs and MP3s are two good examples of digital storage forms.
But to listen to music, digital signals must first be transformed into analog form. This is why DACs are normally incorporated into most music and CD players as well as computer sound cards.
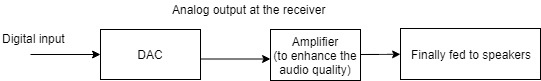
Some Hi-Fi systems are equipped with standalone D2A components that transform the digital outputs into analog line-level signals at the receiver. Consequently, this signal is passed through an amplifier and finally fed into the speakers.
Apart from its audio application, DACs are also incorporated in telephones. They work together with Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) to enable communication via phone call.
At the caller's end, an ADC effectively converts sound into an electrical signal that is transmitted as electromagnetic waves. When these waves reach the receiver, they're transformed back into analog signals by a DAC.
The speaker element converts these analog signals into a sound that can be comprehended by the individual receiving the call.
DAC vs Amplifier
Although DACs and amplifiers perform two distinct functions, they're both crucial components that play a huge role in most electronic devices and audiophiles.
- On one hand, digital to analog converters help to convert digital signals to their analog equivalents. They either come preinstalled or they're purchased separately and used in home theaters, laptops, and headsets.
- Amplifiers, on the other hand, boosts the weak analog signal originating from the DAC, increasing its power so that it can drive speakers. As its name suggests, a preamp amplifies analog signals and later sends it to the speaker elements.
DACs and amplifiers are equally important electronic components that are often used hand-in-hand. Both devices complement each other – the DAC converts digital pulses into analog form, then sends the resultant signal to the amplifier that boosts its power.
However, an amplifier relies on the proper functioning of a DAC in order to function effectively. If the digital to analog converter becomes defective, it inhibits the amplifier from functioning effectively.
In this respect, it's crucial to purchase an external DAC for your laptop and home theater. Also, treat your audiophiles with extreme care to avoid ruining the internal DAC.
DAC vs ADC
An ADC isn't that different from a DAC. However, both devices have contrasting functions. While a DAC converts signals from digital to analog format, an ADC transforms analog signals into digital form.
You might be wondering: what's the purpose of converting analog signals to digital 'zeros and ones'?
There are several reasons why Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) might come in handy.
The main reason is for storage purposes. Digital storage of data is highly preferred over analog storage (especially video and audio data) because the former is highly compressible, seeing as it consists of bitstream sequences.
ADCs are also crucial because they convert analog signals to digital forms for transmission purposes.
For instance, phone conversations must first be converted from their "raw" analog state into digital signals which are then transmitted over the telephone line.
At the other end, these signals are transformed back into analog form using a DAC. To recap, ADCs are utilized by devices that either transport electromagnetic signals (telephones, fax machines) or store data in digital formats (computers, external hard drives).
Both perform the crucial function of converting data from one format to another and thus derive wide-ranging applications in the world of electronics.
DAC vs Sound card
Sound cards are electronic circuits that convert digital signals into analog format and vice versa. These cards have four main components you should know about:
- A DAC that changes digital data into analog forms (sound)
- An ADC that converts analog inputs into digital sequences for storage purposes
- An interface that relies on Peripheral Component Interconnect to link to the computer motherboard
- Input & output connectors that allow users to connect speakers, earpieces or even a mic
Sound cards integrate two functions in one, translating between analog and digital data. These cards are usually integrated directly into computers and other electronics.

Sometimes, a single chip (referred to as CODEC) is built into a sound card rather than having two separate chips. There are numerous sound cards available in the market, some of which bear their own memory and digital signal processor (DSP).
If you're interested in creating high-quality music for parties and live functions, simply purchase a high-end sound card coupled with sturdy external speakers.
The card should be connected to your PC using an appropriate connector. Since DACs are usually contained within a sound card, it would be a great idea to purchase a top-range sound card for your audiophile.
Types of DAC based on applications

#1. Stereo DAC
This type of Digital to Analog Converter is normally designed for home stereo systems. It's versatile and offers users a variety of connection options.
You can utilize an external DAC card if your stereo possesses a digital output. Alternatively, you can use the USB option if your stereo has an inbuilt USB port.
Most stereo connections have two or more high-powered speakers integrated into the system. Adding a stereo DAC provides that extra oomph to your sound.
#2. USB DAC
Today, most electronic devices come with a USB port. The USB DAC is a unique type of Digital to Analog Converter that can be attached on a laptop, desktop PC, stereo unit or any other device that has an inbuilt USB port.
It's quite easy to use: simply plug and play without having to purchase additional drivers.
#3. Hi-Fi DAC
High Fidelity (Hi-Fi) systems have become widely popular among audiophiles because of their exquisite sound reproduction.
Using a Hi-Fi DAC, you can improve the audio resolution of your stereo system. The DAC works by up-sampling low-quality audio signals such as MP3s to produce Hi-Fi renditions. You can purchase this DAC as a separate chip.
#4. Audio DAC
An audio DAC is simply an electronic chip that's used to convert audio signals from their digital forms to analog signals. This chip is either built into an audiophile device by the manufacturer or bought separately by the user.
#5. Outboard DAC
This type of DAC is also referred to as an external DAC because it's purchased separately and then connected to particular devices (such as laptops and stereo systems).
DAC card and USB DAC are two examples of outboard DAC. These converters help to improve audio quality.
#6. Audiophile DAC
If your aim is to enhance the general performance of your audio system, then an audiophile DAC will help.
This type of DAC helps to optimize the Hi-Fi sound quality of your car or home stereo system. You can use an audiophile DAC on your iPod, CD player, iPhone or Mac devices. It also comes in handy when gaming.
Conclusion
DACs have completely revolutionized the way we listen to music.
Today, music fanatics don't have to purchase expensive Hi-Fi systems to enjoy top-quality music – they can simply utilize an outboard DAC to improve the audio quality of their current music devices.

